Collections in Java With Examples
The Java Collections Framework is a collection of interfaces and classes which helps in storing and processing the data efficiently. This framework has several useful classes which have tons of useful functions which makes a programmer task super easy. I have written several tutorials on Collections in Java. All the tutorials are shared with examples and source codes to help you understand better.
Java Collections – Table of Contents
1. ArrayList
2. LinkedList
3. Vector
4. HashSet
5. LinkedHashSet
6. TreeSet
7. HashMap
8. TreeMap
9. LinkedHashMap
10. Hashtable
11. Iterator and ListIterator
12. Comparable and Comparator
13. Java Collections Interview Questions
Collections Framework hierarchy
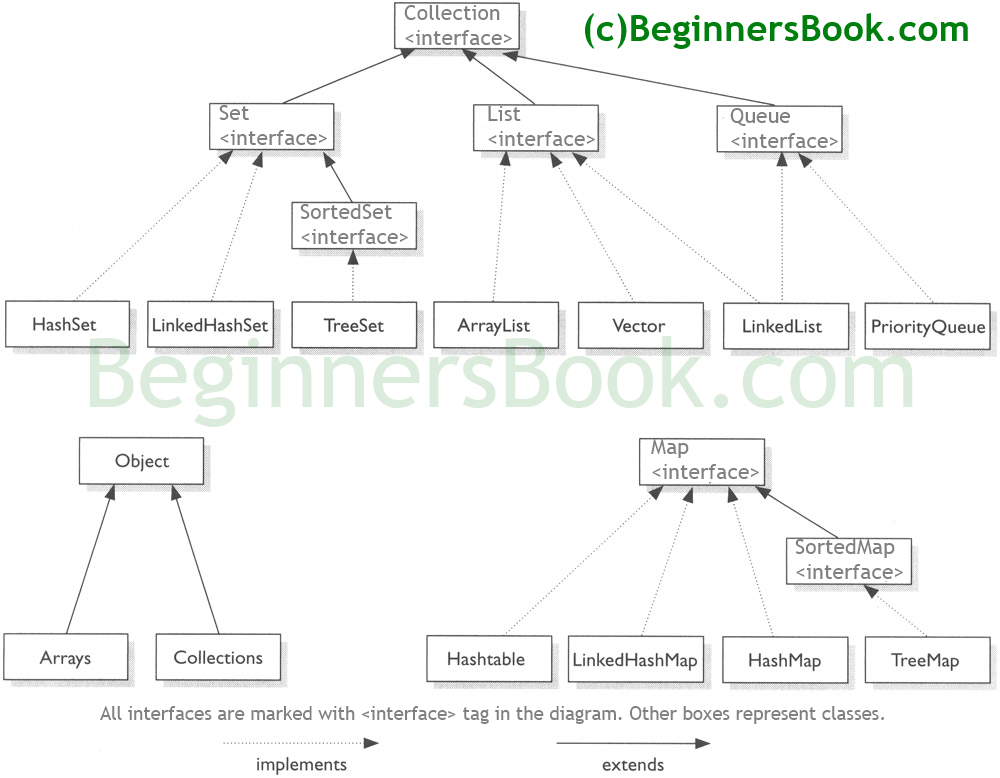
Java Collections – List
A List is an ordered Collection (sometimes called a sequence). Lists may contain duplicate elements. Elements can be inserted or accessed by their position in the list, using a zero-based index.
ArrayList
Here is the list of all the tutorials published on the ArrayList.
ArrayList Basics
- ArrayList in Java
- Initialize ArrayList
- Loop ArrayList
- Find length of ArrayList
ArrayList Sorting
- Sort ArrayList
- Sort ArrayList in Descending order
- Sort ArrayList of Objects using Comparable and Comparator
ArrayList Add/Remove
- Add element to ArrayList
- Add element at particular index of ArrayList
- Append Collection elements to ArrayList
- Copy All List elements to ArrayList
- Insert all the collection elements to the specified position in ArrayList
- Remove element from the specified index in ArrayList
- Remove specified element from ArrayList
Get/Search in ArrayList
- Get Sub List of ArrayList
- Get the index of last occurrence of the element in the ArrayList
- Get element from ArrayList
- Get the index of first occurrence of the element in the ArrayList
- Check whether element exists in ArrayList
Other Tutorials on ArrayList
- Compare two ArrayList
- Synchronize ArrayList
- Swap two elements in ArrayList
- Override toString() method – ArrayList
- Serialize ArrayList
- Join two ArrayList
- Clone ArrayList to another ArrayList
- Make ArrayList Empty
- Check whether ArrayList is empty or not
- Trim the Size of ArrayList
- Replace the value of existing element in ArrayList
- Increase the capacity(size) of ArrayList
ArrayList Conversions:
- Convert ArrayList to String Array
- Convert Array to ArrayList
Differences:
- ArrayList vs Vector
- ArrayList vs HashMap
- ArrayList vs LinkedList
LinkedList
Here is the list of all the tutorials published on the LinkedList.
LinkedList Basics
- LinkedList in Java
- How to iterate LinkedList
LinkedList Add/Remove
- Adding an element to LinkedList
- Add element at specific index in LinkedList
- Add element at the beginning and end of LinkedList
- Adding an element to the front of LinkedList
- Remove First and last elements from LinkedList
- Remove element from specific index
- Remove specified element from LinkedList
- Remove All elements from LinkedList
- Append all the elements of a List to LinkedList
Get/Search in LinkedList
- Get first and last elements from LinkedList
- Get element from specific index of LinkedList
- Search element in LinkedList
- Get Sub list of LinkedList
LinkedList Iterator/ListIterator
- LinkedList Iterator example
- LinkedList ListIterator example
- Iterate a LinkedList in reverse Order
Other Tutorials on LinkedList
- Replace element with a new value in LinkedList
- Check whether a particular element exists in LinkedList
- Clone a LinkedList to another LinkedList
- Get the index of last occurrence of an element in LinkedList
- LinkedList push() and pop() methods
- LinkedList poll(), pollFirst() and pollLast() methods
- LinkedList peek(), peekFirst() and peekLast() methods
Conversion
- Convert LinkedList to ArrayList
- Convert LinkedList to Array
Vector
Here is the list of all the tutorials published on the Vector.
Vector basics
- Vector in Java
- Get sub list from Vector
- Sort Vector using Collections.sort()
- Search element in Vector using index
- Copy Elements of one Vector to another
Remove/Sort/Replace in Vector
- Remove element from Vector
- Remove element from specified index in Vector
- Remove all elements from Vector
- Replace element in Vector
- Set Vector size
Vector -Iterator/ListIterator/Enumeration
- Vector enumeration example
- Vector Iterator example
- Vector ListIterator example
Conversions
- Convert Vector to List
- Convert Vector to ArrayList
- Convert Vector to String Array
Java Collections – Set
A Set is a Collection that cannot contain duplicate elements. There are three main implementations of Set interface: HashSet, TreeSet, and LinkedHashSet. HashSet, which stores its elements in a hash table, is the best-performing implementation; however it makes no guarantees concerning the order of iteration. TreeSet, which stores its elements in a red-black tree, orders its elements based on their values; it is substantially slower than HashSet. LinkedHashSet, which is implemented as a hash table with a linked list running through it, orders its elements based on the order in which they were inserted into the set (insertion-order).
HashSet
Here is the list of all the tutorials published on the HashSet.
- HashSet in Java
- Delete all elements from HashSet
- How to iterate through a HashSet
- Convert a HashSet to an array
- Convert a HashSet to a TreeSet
- Convert HashSet to a List/ArrayList
- HashSet vs HashMap
LinkedHashSet
- LinkedHashSet in Java
- List Vs Set
TreeSet
- TreeSet in Java
- HashSet vs TreeSet
Java Collections – Map
A Map is an object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys. There are three main implementations of Map interfaces: HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap.
HashMap: it makes no guarantees concerning the order of iteration
TreeMap: It stores its elements in a red-black tree, orders its elements based on their values; it is substantially slower than HashMap.
LinkedHashMap: It orders its elements based on the order in which they were inserted into the set (insertion-order).
HashMap
Here is the list of all the tutorials published on the HashMap.
HashMap Basics
- HashMap in Java
- How to iterate HashMap
- Sort HashMap by Keys and values
- Get Size of HashMap
- Remove Key-value mapping from HashMap
- Remove all mapping from HashMap
- How to check if HashMap is empty or not?
Get/Search in HashMap
- Check if particular key exists in HashMap
- Check if particular value exists in HashMap
Serialize/Synchronize
- Serialize HashMap
- Synchronize HashMap
Differences
- HashMap vs Hashtable
- HashSet vs HashMap
Other Tutorials on HashMap
- HashMap Iterator example
- Copy one HashMap to another
- Get value from HashMap using Key
- Get Set view of keys from HashMap
- Clone a HashMap
TreeMap
- TreeMap in Java
- Iterate TreeMap
- Sort TreeMap
- Iterate TreeMap in Reverse order
- Get Sub Map from TreeMap
LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap in Java
Hashtable
Hashtable in Java
Java Collections – Iterator/ListIterator
Both Iterator and ListIterator are used to iterate through elements of a collection class. Using Iterator we can traverse in one direction (forward) while using ListIterator we can traverse the collection class on both the directions(backward and forward). To know more differences between these two refer this article: Difference between Iterator and ListIterator.
- Iterator
- ListIterator
Comparable and Comparator Interfaces
These interfaces are used for sorting objects of user defined class (custom class).
- Comparable interface with example
- Comparator interface with example
Collections Interview Questions
Collections Framework Interview Questions
Reference: Official Document on Collections
Source: https://beginnersbook.com/java-collections-tutorials/
0 Response to "Collections in Java With Examples"
Enviar um comentário